Tendon and ligament injuries, such as Achilles tendonitis, tennis elbow, and rotator cuff strains, can…
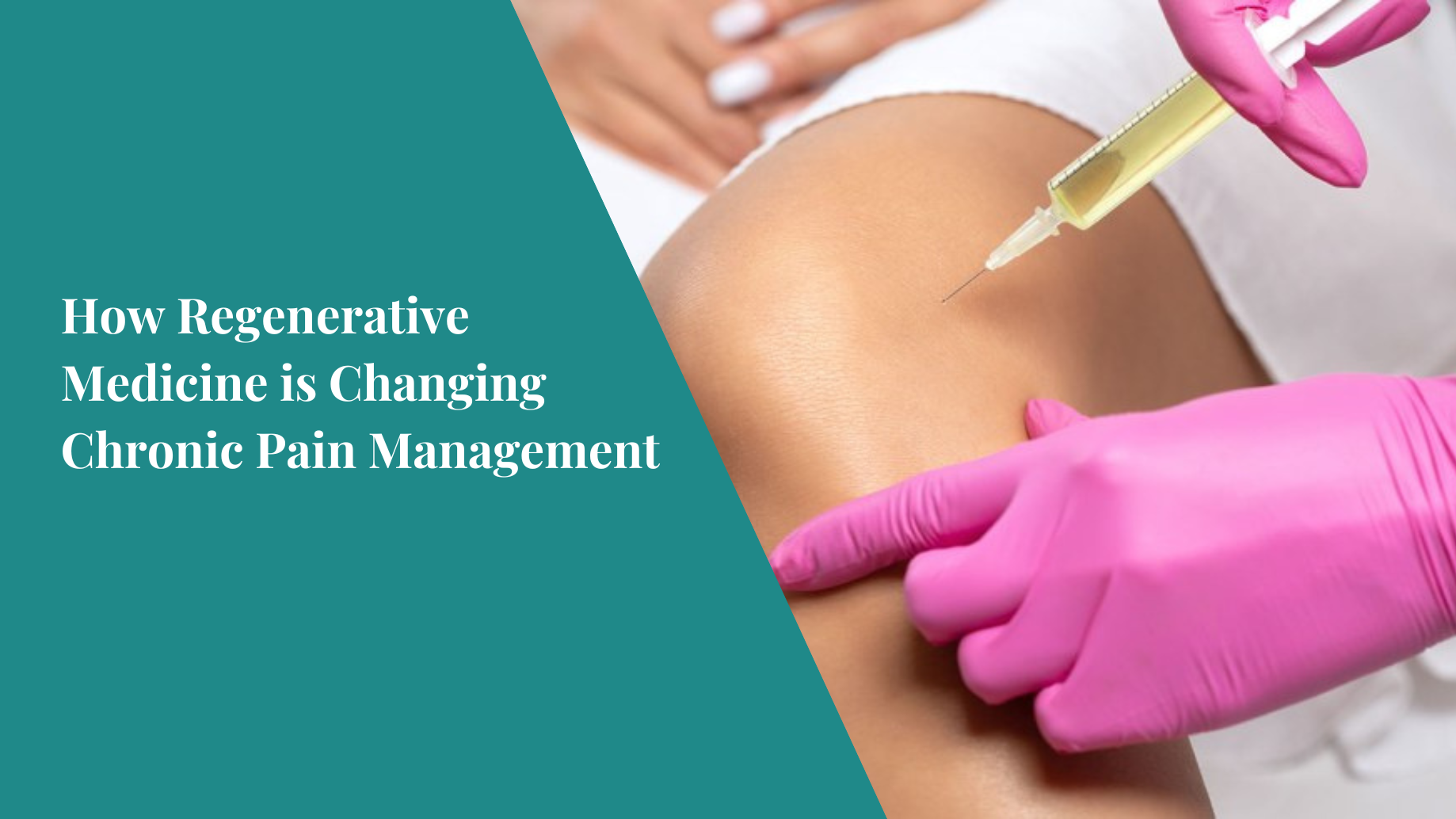
How Regenerative Medicine is Revolutionizing Chronic Pain Management
What if we told you that many traditional pain treatments merely mask symptoms rather than addressing the root cause of chronic pain?
For millions of people living with chronic pain, conventional treatments like painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications often offer only temporary relief. These methods tend to focus on symptom management rather than healing, leaving patients caught in a cycle of discomfort and dependency.
But there’s good news.
Regenerative medicine is changing the way we approach pain management.
This cutting-edge field focuses on stimulating the body’s natural healing processes to repair and regenerate damaged tissues, offering hope for long-term relief and improved quality of life.
In this article, we’ll explore the most promising therapies within regenerative medicine, their benefits, and how they are transforming the landscape of pain management.
At its core, regenerative medicine is an innovative approach to healthcare that leverages the body’s innate ability to heal itself.
Rather than masking symptoms, regenerative therapies aim to address the underlying causes of pain and tissue damage. These treatments are especially promising for chronic pain sufferers who are seeking alternatives to surgery, long-term medication use, or invasive procedures.
By promoting tissue repair and regeneration, regenerative medicine therapies provide an avenue for natural and long-lasting relief.
Here are some of the most notable therapies in this field that are making waves in the medical community.
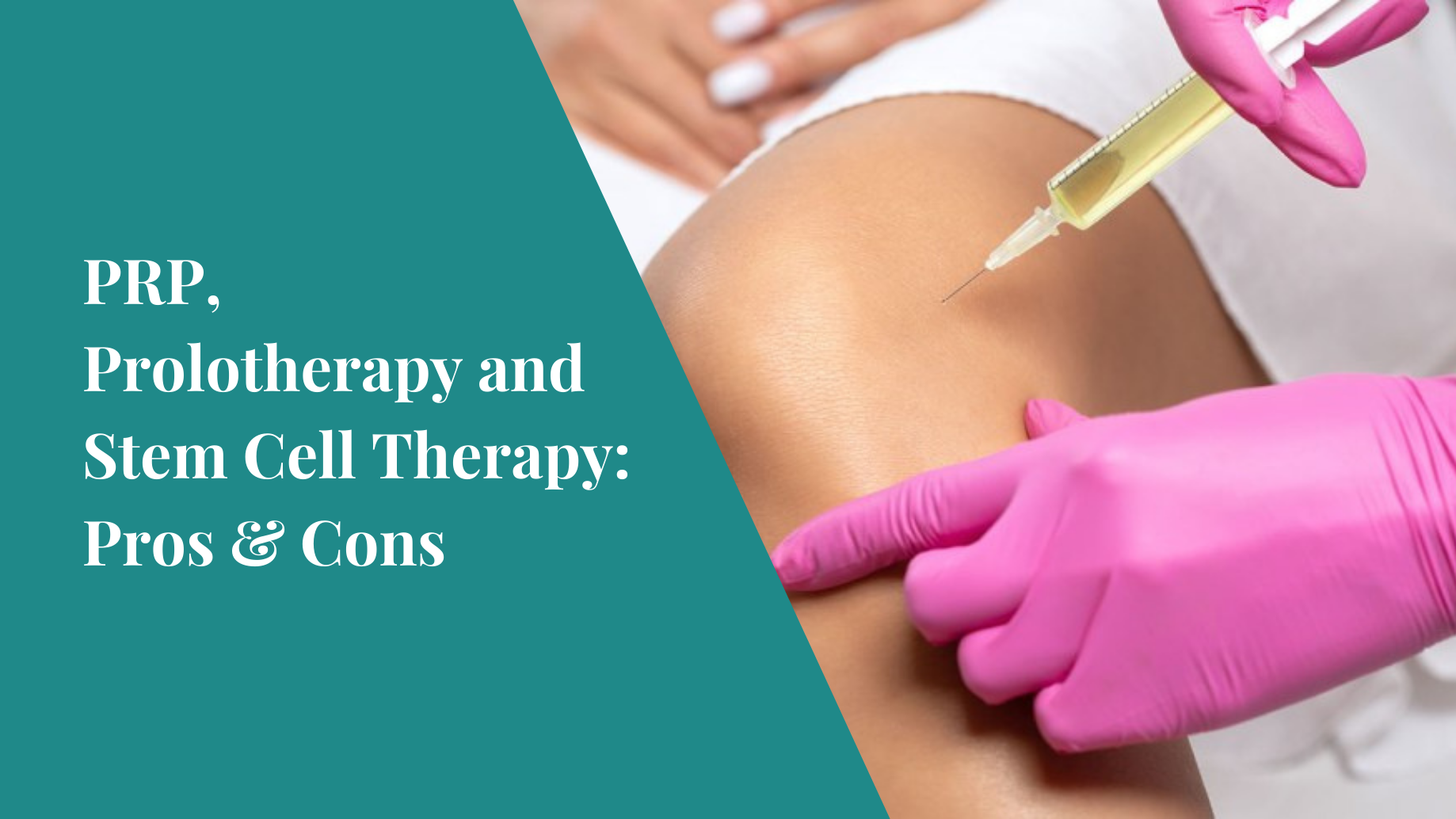
1. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy
What is PRP therapy? Platelet-rich plasma therapy involves extracting a small amount of your blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting this platelet-rich solution into the area of concern. Platelets are rich in growth factors that play a critical role in accelerating tissue repair and regeneration.
Who can benefit? PRP therapy is gaining traction for its effectiveness in treating:
- Osteoarthritis: Reducing inflammation and promoting cartilage repair
- Tendonitis: Facilitating faster healing of tendons
- Muscle injuries: Enhancing recovery in sports-related or overuse injuries
Studies have shown that PRP therapy not only reduces pain but also improves function and mobility, making it a game-changer for patients seeking non-surgical options.
2. Prolotherapy
What is prolotherapy? Prolotherapy, also known as proliferation therapy, involves injecting a dextrose-based solution into the affected area. This injection triggers a mild inflammatory response, which in turn stimulates the body’s natural healing processes.
Key applications:
- Chronic joint pain: Especially in the knees, hips and shoulders
- Ligament injuries: Strengthening weak or damaged ligaments
- Degenerative disc disease: Supporting spine health and reducing pain
Prolotherapy is particularly appealing because it encourages the body to rebuild and strengthen tissue, providing long-term relief rather than temporary symptom suppression.
3. Cell therapy injections
What is cell therapy? Cell therapy utilizes living cells, either harvested from your own body or donor sources, to promote tissue regeneration. These cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various tissue types, making them an invaluable tool for repairing damaged or degenerated areas.
Conditions treated:
- Arthritis: Rebuilding cartilage and reducing joint pain
- Spinal cord injuries: Facilitating nerve repair and regeneration
- Chronic tendinopathies: Addressing persistent tendon injuries
With ongoing advancements in cell therapy research, this treatment has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat complex and chronic pain conditions.
Why choose regenerative medicine?
The benefits of regenerative medicine extend far beyond pain relief. Here’s why more patients and healthcare providers are turning to these therapies:
- Non-invasive: Unlike surgery, regenerative treatments are minimally invasive, reducing recovery time and associated risks.
- Long-lasting results: By addressing the root cause of pain, these therapies offer sustainable relief rather than temporary fixes.
- Reduced dependency on medication: Many patients find they can reduce or eliminate the need for painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Holistic healing: Regenerative medicine emphasizes natural repair processes, aligning with the body’s biology.
Regenerative medicine represents a paradigm shift in how we approach chronic pain and injury recovery.
By stimulating the body’s natural repair mechanisms, these therapies provide a powerful alternative to traditional treatments, offering hope for long-term relief and enhanced quality of life.
If you’re ready to explore how regenerative medicine could transform your pain management journey, don’t hesitate to reach out. Our team is here to guide you every step of the way toward a healthier, pain-free life.
FAQs: Regenerative medicine and pain management
Q: What types of pain conditions can regenerative medicine treat?
A: Regenerative therapies are particularly effective for chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, tendonitis, ligament injuries, degenerative disc disease, and sports injuries.
Q: Are regenerative medicine therapies safe?
A: Yes, these therapies are generally safe when performed by a qualified healthcare provider. Since they often use the patient’s own cells or blood components, the risk of adverse reactions is minimal.
Q: How long does it take to see results?
A: While some patients experience relief within weeks, the full benefits of regenerative treatments may take several months as the body gradually repairs and regenerates tissue.
Q: Is regenerative medicine covered by insurance?
A: Coverage varies depending on the therapy and provider. It’s important to consult your insurance company and healthcare provider for specific details.
Q: Can regenerative medicine replace surgery?
A: In many cases, regenerative medicine can serve as a viable alternative to surgery, particularly for conditions like joint pain and tendon injuries. However, severe cases may still require surgical intervention.